How to use the tool
This section describes how you run the habitat models, and how you can inspect and change the settings for a model.
After running a simulation in RegWise or for an optimization result in PlanWise, you can start the tool from the Tools-menu. Since the tool takes into account spatial relations between treatment units, you cannot use results from this tool as input data in an optimization model. You can only do this as post-evaluation step. In PlanWise, the optimization model should either be MIP (by setting the x-variables for to binary), which requires an efficient solver for large problems. Alternatively, ensure that you have activated "Round the integer" in the optimization settings.
The habitat model tool requires that you have imported a forest map, and that you have done a simulation or optimization in RegWise or PlanWise. You can import the forest map after running a simulation or optimization problem, so there is no need to rerun a TPG-simulation just because no map was present when running it.
You open the form in the Tools-menu:
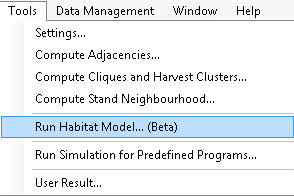
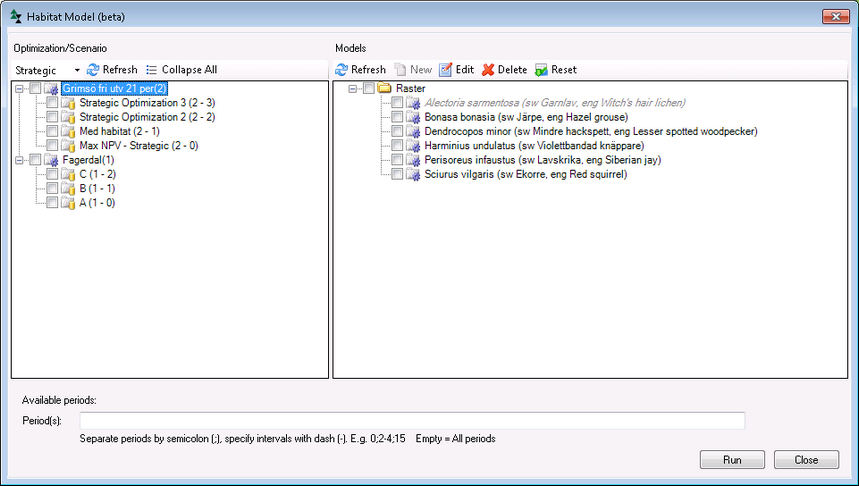
Figure 1. The main form for the habitat models can be found under the Tools menu > Run Habitat Model.
On the left side the existing optimization results or simulation results are listed, of which you can choose or or more to be evaluated.
On the right side the habitat models are listed.
A raster-based habitat model converts the polygons to a raster and can take into account both the forest state at a certain point (cell), and the environment around the cell. To be classified as suitable habitat, both the cell itself and, depending on the model, its surrounding must meet certain requirements. These differs between models and can be modified by the user. In later version you will also be able to create new models.
Requirements on the surroundings can be adjusted by specifying how large the neighborhood is (radius), and the proportion of the neighborhood that must contain certain features.
To view and change settings for a model, double click on it or select it and choose Edit (right hand side list in figure 1).
Model type: Type av model: Raster- or vector-based
Cell size: Here you set the resolution of the raster cell grid. The smaller the cell size, the smaller the transformation errors. However, the execution times increases the smaller the cell size is.
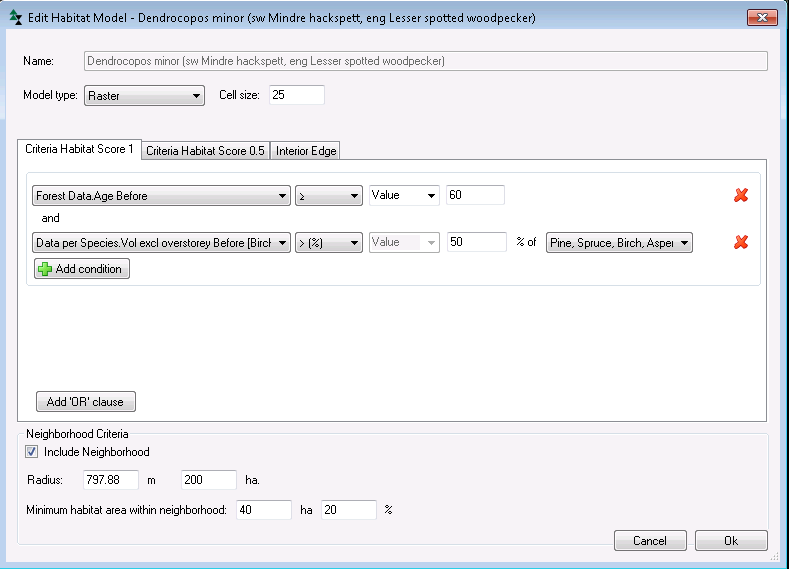
Criteria Habitat Score 1: Enter conditional requirements in this tab for a stand to considered as suitable habitat. These scores are used to determine both if a grid cell can be finally classified as a habitat, and whether a cell can be considered neighborhood habitat. The formulation of conditions is analogous to how conditions are created in the Heureka report builder.
Criteria Habitat Score 0.5: In this tab, enter conditional requirements for a stand that does not qualify as perfect habitat (Score 1), but is "half as suitable" . The values are used in the same way as Score 1-values. Two cells with Score 0.5 has the same habitat value on cell with value 1. Note! If you do not enter conditions for Score 0.5, then all cells that not qualify for Score 1 will be assigned Score 0.5. To avoid this, enter the same condition for 0.5 as for 1.
Interior Edge: In this tab, you will be able to define edge zone effects on habitat suitability. If a raster cell is located within a certain distance from a stand's border, and near an adjacent stand that is for example open land or a young plantation, the habitat score is adjusted with the factor you enter in the Factor field.
Include Neighborhood: Check this box to make the model spatially dependent. In this case the model takes into account the abundance of suitable habitat in the neighborhood defined of a subject cell when determining if the cell qualifies as habitat. If you uncheck the box the habitat model becomes a spatially independent (stand-level) model.
Radius: Radius of the circle that defines the neighborhood size. If you enter the neighborhood size in area units (in hectares), the radius is calculated automatically.
Minimum habitat area within neighborhood: This parameter is the area within a neighborhood (or area percentage if the neighborhood area) of suitable habitat required for a cell to be qualified as habitat. A raster cell is part of its own neighborhood.
|
This model type is not available at the moment.
|
Se även: text